Decline in Public Satisfaction with the NHS
In the United Kingdom, the National Health Service (NHS) stands as a fundamental pillar of public health, offering essential medical services to millions. However, recent findings from the British Social Attitudes survey paint a concerning picture. Public satisfaction with the NHS has reached its lowest recorded level, reflecting growing concerns over waiting times, staff shortages, and overall service quality. In this article, we delve into the key findings of the survey, explore the reasons behind the decline in satisfaction, and discuss potential avenues for improvement.
The Survey Results
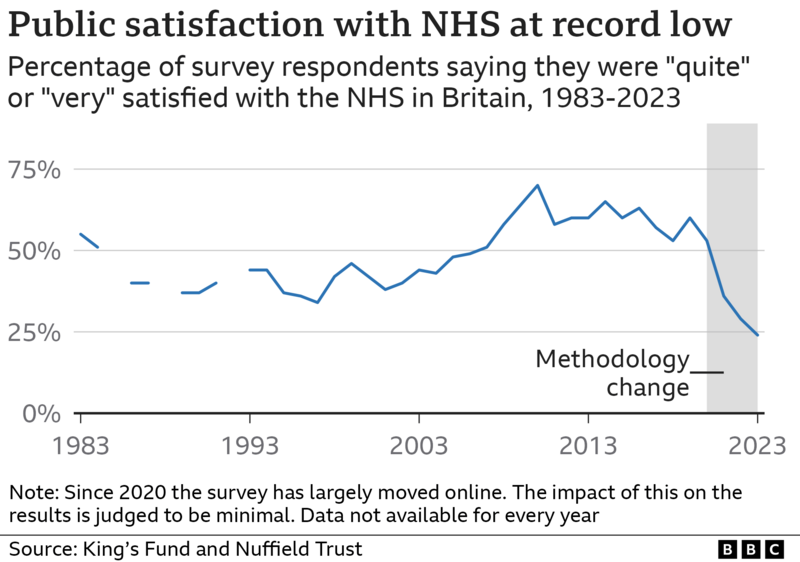
According to the British Social Attitudes survey conducted in 2023, only 24% of respondents expressed satisfaction with the NHS, marking a five-percentage-point drop from the previous year. This figure starkly contrasts with the peak satisfaction rate of 70% recorded in 2010. The survey, conducted by the National Centre for Social Research across England, Wales, and Scotland, polled over 3,000 individuals, providing valuable insights into public sentiment towards the healthcare system.
Key Concerns
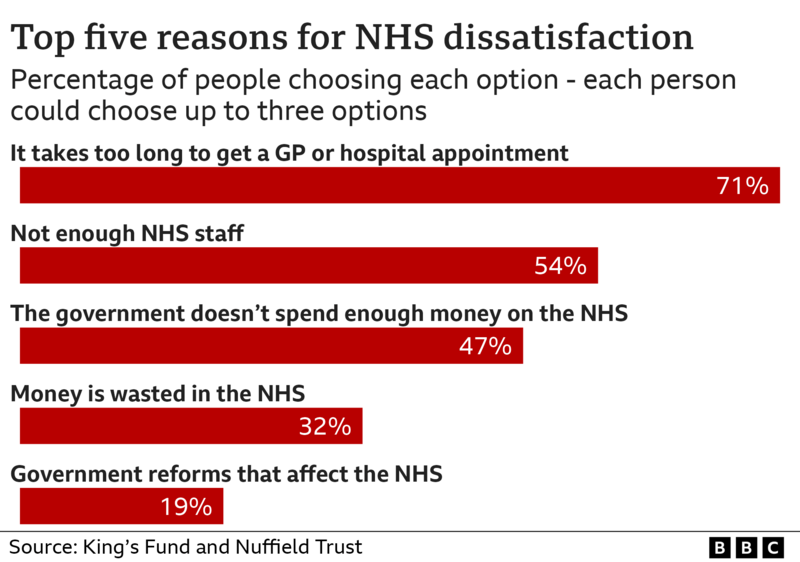
Several factors contribute to the declining satisfaction levels among the public:
-
Long waiting times for medical appointments and procedures remain a significant source of frustration for patients.
-
The NHS faces persistent challenges in recruiting and retaining healthcare professionals, leading to understaffed facilities and overworked staff.
-
Insufficient funding and resources strain the healthcare system, impacting service quality and patient outcomes.
Impact on Core Services
The survey highlights specific areas of dissatisfaction within the NHS:
-
Public satisfaction with A&E services remains low, reflecting concerns over overcrowding and lengthy waiting times.
-
Dental services also receive low satisfaction ratings, indicating potential issues with accessibility and quality of care.
Social Care
In addition to healthcare services, public satisfaction with social care has plummeted to 13%, the lowest since the survey's inception. Similar to healthcare, long waiting times, staffing shortages, and funding constraints contribute to dissatisfaction in the social care sector.
Public Opinion on Government Action
When asked about government interventions, nearly half of respondents (48%) supported increased taxes and spending on the NHS. However, a significant portion (42%) preferred maintaining current levels of taxation and spending. These divergent views underscore the complexity of addressing healthcare challenges through policy measures.
Industry Perspectives
Rory Deighton, the NHS Confederation's acute network director, acknowledges the challenges faced by both patients and healthcare professionals. He emphasises the need for concerted efforts to improve access to primary care and reduce waiting lists. Increased investment in hospitals, GP surgeries, and social care is deemed essential for addressing systemic issues.
Call for Action
Healthcare organisations, such as the Nuffield Trust and the Royal College of Nursing, stress the urgency of addressing the NHS's shortcomings. Political parties are urged to prioritise healthcare reform, focusing on enhancing service quality, reducing waiting times, and ensuring equitable access to care.
Government Response
While acknowledging the survey findings, the Department of Health and Social Care in England highlights ongoing efforts to improve NHS performance. Investment in key areas like GP services demonstrates a commitment to addressing systemic challenges. Similarly, the Scottish and Welsh governments emphasise their dedication to enhancing healthcare despite budgetary constraints.
Conclusion
The decline in public satisfaction with the NHS reflects deep-rooted challenges facing the healthcare system. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach, involving increased investment, workforce development, and policy reforms. By listening to patient experiences, collaborating with healthcare professionals, and prioritising public health, stakeholders can work towards rebuilding trust and ensuring the NHS delivers on its promise of quality care for all.
Private Medical Insurance as a Solution
While systemic issues within the NHS are being addressed, increasing numbers of individuals are exploring alternatives like Private Medical Insurance to alleviate immediate concerns. PMI offers access to private healthcare services, reducing wait times and providing additional health choices for patients.
